Your Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) Guide
SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) is one of the most powerful tools available to your business. That’s why we’ve built ab SEO Guide to get you started.

What is Search Engine Optimisation?
All major search engines such as Google, Bing and Yahoo have search engine results pages (SERPs), where web pages and other content are displayed and ranked based on what the search engine considers most relevant to users.
Almost all the sales leads we get for our CRM system come through Google search, at no marginal cost to ourselves. In this article, we look at the fundamentals of Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) and how it can benefit your business.
SEO Fundamentals
Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs)
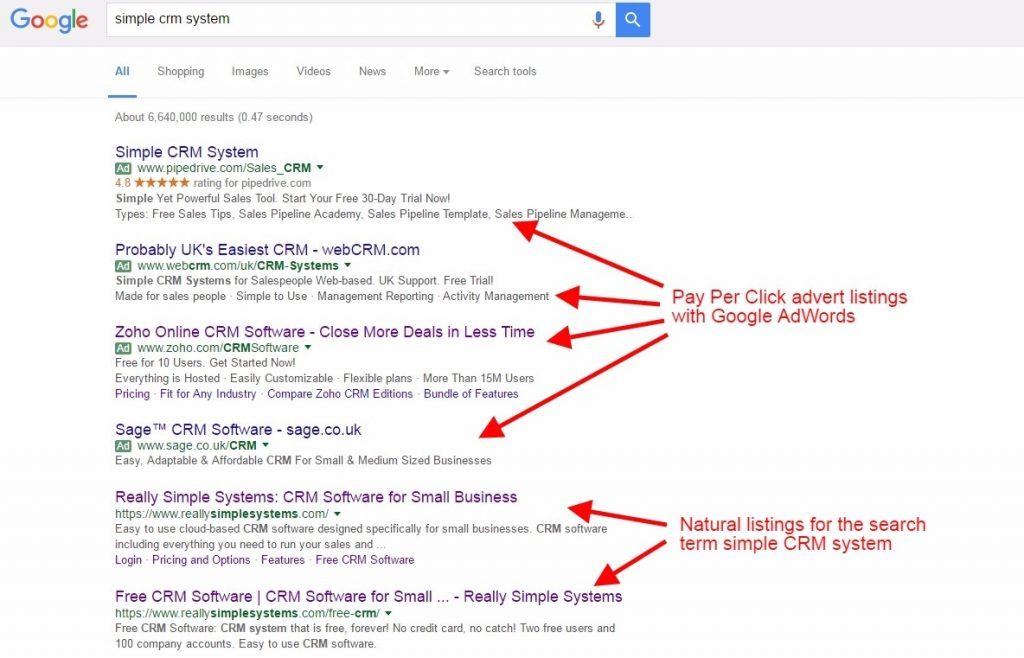
When you make a search, Google will return the sites that it thinks best fit your query in the “organic” or “natural” search results. Google will also show advertisements for other sites, usually three at the top of the results, before the natural results, and up to eight more on the right-hand side. Google makes a small effort to differentiate the ads from the natural results, either by having a slightly different background for them or showing a little green “Ad” sign next to them.
Many people, however, have no idea that there is a difference between natural results and ads. To benefit from Google Ads, the basic rule is that you need to be on page one of the search results as few people click through to subsequent pages. Some people ignore all the ads in the knowledge that those sites didn’t get there because they were any good but because they paid money.
Choosing Your SEO Keywords
Your keywords are the terms that you’ll be optimising your website for. They are the words or phrases that, when somebody searches for them in Google, you want your website to come up in the results. For example, for SpotlerCRM our main keywords are “Simple CRM”, “Free CRM” followed by “Online CRM”, “Best CRM” and “Small Business CRM”. These keywords are known as “short tail keywords” and are search phrases with only one or two words. Their length makes searches less specific, however, they are more likely to drive high levels of traffic than searches with more words, or “long tail keywords”.
Long tail keywords are phrases made up of 3 or more words, which tend to have less traffic because their searches are more specific. Some examples of our long tail keywords are “What is customer relationship management” or “What is the best CRM for the finance industry”. Though long tail keywords drive less traffic, the traffic is more relevant traffic and they tend to have higher click-through rates.
Discovering Keywords
You may think you know what your keywords are, however what you think your keywords are might not be what prospects are searching for. For example, when we first started out we optimised our site for “Online CRM”. Then the word “Cloud” started being used and our industry started using the words “Cloud CRM”. So, we changed the optimisation of the site from “Online CRM” to “Cloud CRM”. After a week we thought we’d run a check and discovered that ten times more searches were being done for “Online CRM” than “Cloud CRM”, and so quickly set it back to that.
It is also a good idea to look at your competitors’ sites and see what keywords they are using. Look at the HTML source of the page to see what the Title, Meta Description and H1 tags are.
Take inspiration from this but do not copy it directly, Google hates plagiarism.
To find out what people are searching for, you can use the Google Keyword Tool. This will show you how many searches a month there are for a given keyword and will suggest alternative keywords for you to look at. This tool used to be freely available but now it can only be accessed if you have a Google Ads account.
You can sanity check the keywords by typing them into Google search. If your competitors have done their SEO correctly, they should turn up in the results!
Once you’ve decided what your keywords will be, you can start to optimise your site for them.
SEO Factors
We’ve listed key optimisation factors to consider when you start optimising your website. These factors include influencers for both your search results through algorithms as well as the user experience influences.
These factors should be applied to all your web pages; however, they are especially important for your key landing pages such as your Homepage:
Title Tags
Your title tag is what appears as the clickable blue link on the search engine results pages (SERPs). They are important to both viewers and Google algorithms. Search engines use them to help decipher what the web page is about, while the viewer decides how relevant your page is to their search and if they should click on your link.

A good title tag will be an accurate and concise description of a page’s content, do this well and you will see an improvement in visibility and click-through rates. Google best practice recommends that title tag length should be a maximum of 65 characters.
As an example, our Title Tag for our home page is:
Best CRM Software for Small Business
It tells our viewers what we want them to know, our brand name and encourages them to find out why we provide the best CRM software!
Meta-Description Tags
Meta Descriptions are the text displayed below your title tag and are used to summarise your web page in SERPs. Try to keep descriptions around 160 characters, however Google recommends a length between 50-300 characters.
Meta Descriptions are not used by search engine algorithms; however, they are important for viewers so try and include a call to action to encourage clicks!
Heading Tags: H1’s, H2’s, etc.
A heading tag is a small line of code in your web page title that let’s algorithms know what the page is about. You can mark headings from 1-6 (e.g. H1, H2). H1 is your main title, H2’s are your subtitles, and so on. They should contain your targeted keywords and should be relevant to your web page content.
H2 tags are subheadings and should contain similar keywords to your H1 tag, this helps Google understand the structure of your content. You can include further heading tags, however search engines generally prioritise H1s-2s. You can only have one H1 tag, while you can have multiples of other heading tags (2-6).
An example of one of our H1 tags is: “What is CRM?”

If you are using a tool such as WordPress to maintain your site, maybe with an SEO plug-in, make sure you look at the source HTML that is generated to make sure that all the tags are being created correctly.
Content
The text on the page should include all your keywords somehow woven into natural English so the page reads well. You can use the keywords multiple times, but don’t overdo it as Google doesn’t like “keyword stuffing” and will penalise you if you do that.
Make sure that your content is relevant and informative to encourage further exploration of your website. Google recommends a copy length of 800 words for the best SEO results.
Alt Image Text
The Alt Image attribute is a line of text that provides alternative information for an image if a user for some reason cannot view it. Google algorithms can’t read the text in images either, so putting keywords in images will have no effect. You can use the alt text on the image to include keywords, though.
Once you have included these SEO factors on your key landing pages, you can think about applying them to the other pages in your website. All pages should have different titles, meta descriptions, and H1 tags. Ideally, each page should focus on one of your main keywords. You should also use that keyword in the page URL, for example, https://www.reallysimplesystems.com/free-crm/
Mobile Friendly Optimisation
Make sure that your website is built to be adaptive or mobile-friendly. Google algorithms now prioritise mobile-friendly websites over those that are not in search results. You can test your website using Google’s Mobile Friendly Testing Tool.

Measuring SEO
You’ll want to measure the SEO improvements you’ve made to your website. Luckily there is a huge array of tools available to do so.
As every business is different, you can select what data is relevant for you to track, however, there are three key performance indicators (KPIs) that should always be considered when measuring your SEO activity:

Not only can the information gathered from these three KPIs enable you to accurately measure your website’s SEO performance, they can also provide you with actionable data to improve your website over time.
If you haven’t done so already, sign up to Google Search Console (used to be call Webmaster Tools). You’ll need to register, and then find out where your site ranks for your keywords. Keep a record of where each keyword ranks, and you’ll see if your SEO activity is working. You can also sign up for tools that offer you in-depth reports such as Moz or SEMrush, and you should monitor your website’s traffic activity on Google Analytics.
Warning – Don’t rely on doing a search yourself to see where you turn up. Google personalises search results, and if it thinks you like a website, it will start showing it higher up just for you. If you want to do this, use a clean browser with history and cookies deleted.
SEO Summary
That’s a quick do-it-yourself guide to starting to optimise your site for Google and other search engines. The next steps include getting incoming links and continually adding new content, plus more advanced techniques. These will be covered in a subsequent article.
Really Simple Systems is now Spotler CRM
The same great technology, a CRM platform that is focused on the needs of B2B marketers, provided by the same great team, at a great price!